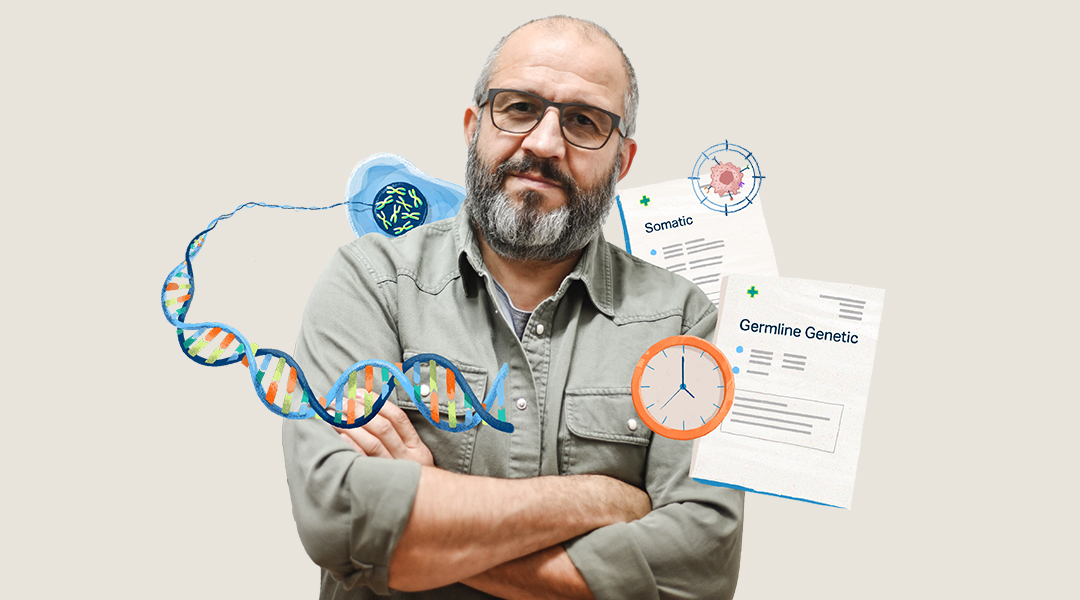
What are somatic and germline genetic testing?

Advanced prostate cancer is different for everyone.
A treatment that works well for one person may not work for someone else. Fortunately, specific genetic tests are available that can help you and your doctor choose the right treatment for you.
Two main genetic tests are used for this purpose. Somatic testing looks for changes in the genes and proteins of your tumor cells. Germline genetic testing looks at your healthy cells for genetic information inherited from your parents. If you have advanced prostate cancer, getting both types of tests will give you and your doctor the most complete understanding of your treatment options.
These tests also provide important information about how your disease might progress, your eligibility for clinical trials of new treatments, and whether you and your family may be at increased risk for prostate cancer and certain other cancers. This helps everyone make informed choices to support the best possible health outcomes.
What is DNA?
DNA is the chemical code that tells your body how to look, grow, and work. Every cell in your body has a copy (except your red blood cells).
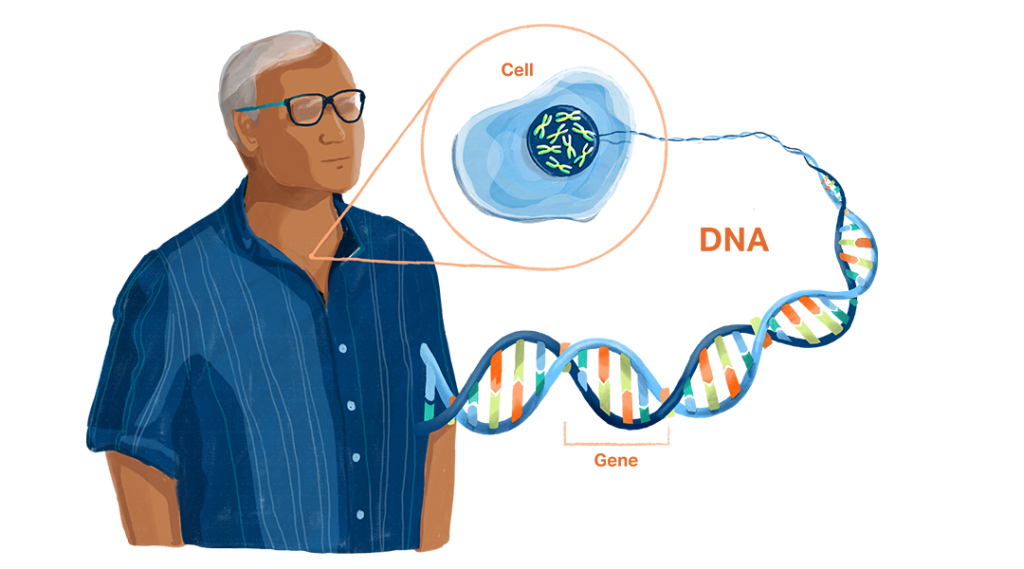
What is a gene?
DNA is made up of thousands of bundles called genes. Some genes control physical features, like eye and hair color. Others affect how your body works.
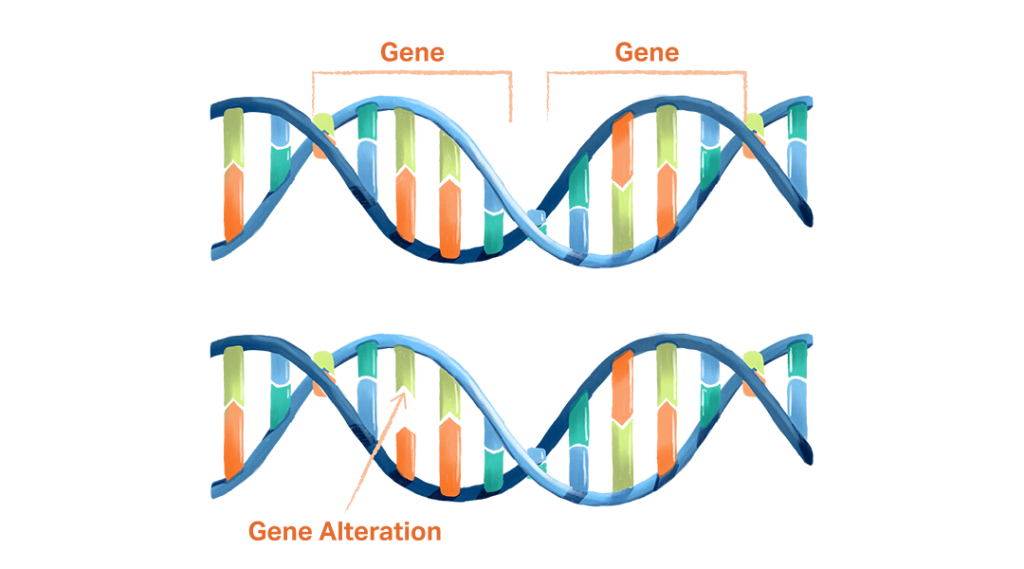
What is a gene alteration?
A gene alteration is a permanent change in the DNA of a gene. Gene alterations can be inherited from a parent, or can occur after birth.
There are millions of different gene alterations. Some gene alterations do not affect how your body works. Others increase your risk of cancer or other diseases, make a disease more aggressive, or affect how well certain treatments work.
What are somatic and germline genetic testing?
Somatic and germline genetic testing look for gene alterations and related changes that provide important information about your prostate cancer. There are two types of tests:
Somatic testing
Somatic testing looks for specific changes in the DNA and proteins of your tumor cells that can drive tumor growth and treatment response. This test uses tumor tissue from a prostate biopsy or surgery. If tumor tissue is unavailable, a blood sample can be tested for circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Somatic testing is sometimes called genomic testing, tumor testing, or biomarker testing. These terms all mean the same thing.
Germline genetic testing
Germline genetic testing looks at your healthy cells for gene alterations you inherited from your parents. The test is done on a saliva or blood sample. Germline genetic testing is sometimes called hereditary testing or inherited cancer risk gene testing. These terms all mean the same thing.
Both types of tests use broad (multigene) panels to look at many different genes at the same time. These genes include homologous recombination repair (HRR) genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, mismatch repair (MMR) genes, and many others.
Somatic testing looks at the genes and proteins of your tumor cells. Germline genetic testing looks at genetic information you inherit from your parents. If you have advanced prostate cancer, getting both tests can help show the best treatment for you.